Many people have a negative perception of bankruptcy, but it can actually be an effective method for getting out of debt. Though bankruptcy filings are public records and private employers may view that information when considering job applicants, there are certain restrictions on what they can consider during the evaluation process. It is also possible to obtain credit after filing for bankruptcy, as many lenders understand the financial struggles of those who have gone through this.
Despite the impact that bankruptcy may have on job searches and credit options, there are still ways to become financially secure by overcoming any obstacles you may encounter along the way.
The Reality of Bankruptcy

Bankruptcy is a legal process in which an individual or business seeks relief from their debts. Many people view bankruptcy as a stigma, but the reality of filing bankruptcy may be much better than the stigma portrays. The Fair Credit Reporting Act states that any bankruptcy filing on a credit check must be removed ten years after the date of the filing, so it won’t affect your credit score forever.
Additionally, most employers cannot use this information when conducting background checks, meaning it can’t prevent you from getting a job. Bankruptcy is not something to take lightly, but understanding how it works and how it affects your life can help ease any worries associated with it.
What is Bankruptcy?

For individuals or businesses that are struggling with debt repayment, bankruptcy is a legal option that can provide relief. To file for bankruptcy, one must petition the bankruptcy court and provide evidence of their financial situation to see if they qualify under the United States Bankruptcy Code.
For those who’ve filed bankruptcy, it is possible to discharge or reorganize certain types of debt (such as debt from medical bills). The two most common types are Chapter 7 and Chapter 13; however, there are other lesser-known forms of bankruptcy that may be more suitable for resolving different kinds of issues.
What Are the Different Types of Bankruptcy?

When considering bankruptcy as a form of debt relief, it is important to understand the implications and potential long-term consequences. Filing for bankruptcy offers individuals or businesses the ability to reduce or eliminate their debt, but there are various requirements depending on the type chosen.
However, filing for bankruptcy will impact your credit score, and (although it is unlikely) it could potentially affect your employment status. It is highly recommended that anyone considering filing for bankruptcy speak with an experienced bankruptcy lawyer who specializes in bankruptcy law.
How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Job?

Filing for bankruptcy can have an impact on someone’s job prospects and current employment. Credit reports are often used by employers to make hiring decisions, and if the prospective job applicant has filed for bankruptcy, it is likely that this history will appear on their credit report.
If an employer sees a bankruptcy filing when viewing a potential employee’s credit report, they may decide against offering them the position or even terminate them from their current employment. However, there are certain legal rights that protect job applicants and employees after they have declared bankruptcy. In the next section, we’ll delve into these rights further so that you can understand how bankruptcy might affect your job situation.
Employment Rights After Bankruptcy

Filing for bankruptcy can be overwhelming, but federal law gives workers certain rights and protections. These rights can help with employment after bankruptcy. An employer cannot reduce an employee’s wages or benefits due to their financial situation. If an employer fires an employee solely because of their bankruptcy filing, this violates the employee’s rights. Bankruptcy may not prevent a person from getting a new job or security clearance.
Employers’ Responsibilities When It Comes to Bankruptcy

When it comes to the bankruptcy of an employee, employers are responsible for providing a supportive work environment and understanding all their rights.
This includes not discriminating against them based on their financial situation, as well as refraining from taking action that could harm the employee or put them in a financially vulnerable position.
Overall, it is important for employers to be supportive of employees during the bankruptcy process and help their employees navigate through it with respect and dignity.
Bankruptcy for Jobs in the Private Sector
State and local government agencies provide protection to employees in the private sector who have filed for bankruptcy when it comes to their job rights. For certain jobs within the private sector, a background check may be required, and if an individual has filed for bankruptcy, employers must still consider them for the job, unless they don’t meet other requirements such as having the necessary security clearance.
Employers must take into account an individual’s bankruptcy case when hiring or terminating them, as discrimination against someone based on having declared bankruptcy is prohibited. It is important for any employer in the private sector to understand applicable laws and regulations with respect to bankruptcies among applicants and employees.
However, there are certain cases in which a private employer may deny employment, such as if an applicant has violated any law or failed to fulfill an obligation related to their previous job. To ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, employers should make sure they understand all relevant information regarding employees who have filed for bankruptcy and take any necessary measures.
How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Credit?

Bankruptcy can be a scary thought, especially when it comes to worrying about having bad credit. But there is hope! It’s important to understand how bankruptcy can affect your credit history, as this can determine how long it will take you to recover from filing for bankruptcy protection.
In the following section, “How Bankruptcy Affects Your Credit Score,” we’ll dive into the details of what happens when you file for bankruptcy and why it is important to keep an eye on your credit score after filing. By understanding more about the process of filing for bankruptcy and the effects on your credit score, you’ll be able to make informed decisions that are best for your financial future.
How Bankruptcy Affects Your Credit Score
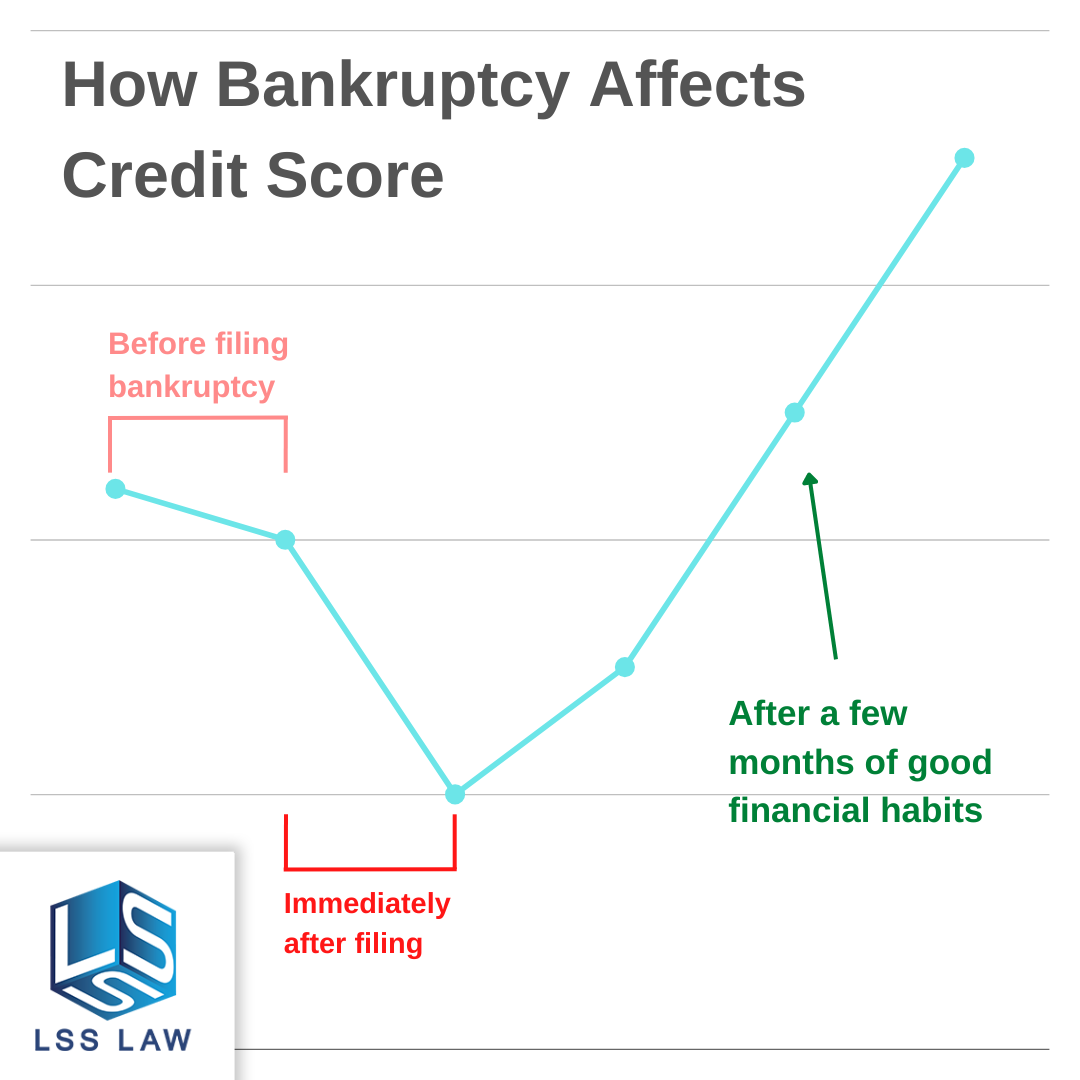
Bankruptcy has a negative connotation, but in reality, it might be the best financial decision you’ve ever made (as long as it’s done right, preferably with a reputable bankruptcy law firm). Bankruptcy can help financially troubled people start over. Bankruptcy resets your credit score, but you should know how it affects it before choosing it. In this section of our blog, we will explain how bankruptcy affects your credit score and some of the underlying issues with credit checks and applying for loans or credit cards after bankruptcy.
Knowing how bankruptcy will affect your credit score is crucial. Bankruptcy will lower your credit score by 80–150 points and stay on your report for seven to ten years. However, bankruptcy has some benefits. After bankruptcy, you may qualify for new credit. After bankruptcy, timely payments on loans and debts can improve your credit score. When done responsibly, bankruptcy can offer a fresh start.
Fun fact: Most people who file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy actually see an INCREASE in their credit score 180 days after filing when compared to the period of time before they filed. Just think about it, you are erasing the debts that are constantly weighing your credit score down, and making room for good financial habits to actually make a difference.
Rebuilding Your Credit After Bankruptcy

The decision to file bankruptcy is a difficult decision for anyone to make, but it can be a very important step towards regaining control of your finances. At LSS Law, we understand the importance of rebuilding credit after filing for bankruptcy and will work with you to help you develop strategies to avoid future financial problems.
One of the best ways to rebuild credit after bankruptcy is to pay all current bills on time, keep balances low on credit cards and other revolving credit accounts, and apply for new credit in small amounts. Our attorneys are here to help individuals experiencing bankruptcy issues by offering advice regarding how they can rebuild their credit after filing with us. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you need help creating a plan for rebuilding your finances.
Contact LSS Law to Learn More About Bankruptcy

If you are considering filing for bankruptcy, it is important to hire an experienced attorney who can help guide you through the process. At LSS Law, we understand that most situations involving bankruptcy involve sensitive information and can be stressful. That is why we wholeheartedly encourage research to make the process as easy and stress-free as possible by providing our clients with access to experienced attorneys who have a deep understanding of all aspects of bankruptcy procedures.
If you would like to learn more about how our team can help you in your situation, please don’t hesitate to contact us. You can call us at 954-466-0541, email us at info@lss.law, or visit our Contact Us page at lss.law/contact to schedule a no-cost bankruptcy Strategy Session with one of our experienced attorneys today!
FAQs | How Does Bankruptcy Affect Your Job and Future Credit?

You’ve come to the right place to learn how bankruptcy affects your job and credit. Below are bankruptcy and employment/creditworthiness FAQs. Understand how bankruptcy may affect your job search and credit application. Your bankruptcy may disqualify you from employment if the employer has a negative view of bankruptcy. Bankruptcy can stay on your credit report for years, which may deter lenders. Please read the most frequently asked questions below for more information.
Can bankruptcy affect my job?
Bankruptcy can potentially affect a person’s job if a private employer chooses to include it in their hiring criteria. While most employers do not ask about bankruptcy or even consider it during the hiring process, some are allowed to search a potential employee’s credit history and look for any signs of financial distress.
If they find proof of bankruptcy, they could potentially choose not to hire that individual due to their perceived financial instability. Additionally, wage garnishment is another way in which a person’s job could be affected by bankruptcy; if an individual has unpaid debts, creditors can sometimes petition the court for permission to garnish wages from an employer in order to collect what is owed. It is important to note, however, that federal law does limit how much can be taken from each paycheck and protects certain basic needs expenses from being seized.
Can my employer find out about my bankruptcy?
Before filing for bankruptcy, it is essential to determine whether or not your employer may be able to find out. Generally, employers are unable to access your credit report and are unaware if you have filed for bankruptcy.
However, there are a few exceptions. For example:
- If you work in a field that requires licensing or certification from a local government agency;
- Certain employers may be able to access your credit report for a valid business purpose;
- And it all depends on the state’s laws.
Therefore, it is important to consult an attorney to double-check that your employer won’t find out about your bankruptcy before taking any steps.
Will bankruptcy show up on my credit report?
When considering bankruptcy, it is important to understand all of the implications before making a decision. Depending on whether you file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy, it can remain on your credit report for up to 10 years.
Additionally, once a collection agency has been notified of the filing of either type of bankruptcy, they are legally required to delete any negative items related to that account from all three major credit bureaus. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of how filing for either type of bankruptcy may affect your credit report.
Can I get credit after filing for bankruptcy?
Rebuilding your credit score and obtaining credit after a bankruptcy filing is possible, although it may take some time and effort. To begin rebuilding your credit, you should make all payments on time each month and consider taking out a secured credit card that reports to the major credit bureaus or applying for a loan from a credit union if eligible.
With these options, you can build your credit while also gaining financial flexibility and security. Remember that building good credit takes consistency and dedication, but it is definitely achievable with hard work.
How long does it take to rebuild credit after bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy recovery requires credit repair. Unfortunately, there is no standard timeframe for credit repair. The type of bankruptcy and the individual’s financial situation before filing affect how long it takes.
Rebuilding credit after bankruptcy takes time and planning. Individuals must open new lines of credit, make on-time payments, keep debt low, and closely monitor their credit reports to ensure accuracy. After bankruptcy, people can start rebuilding their credit with proper planning and determination.





